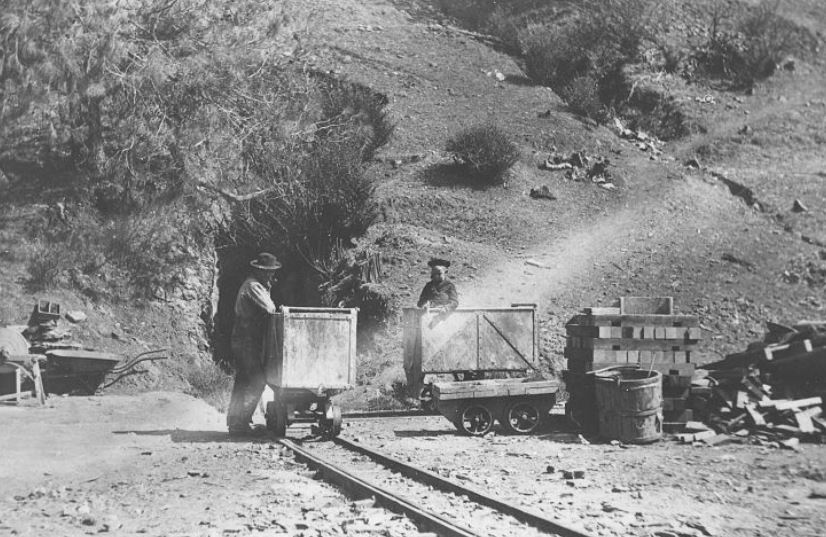
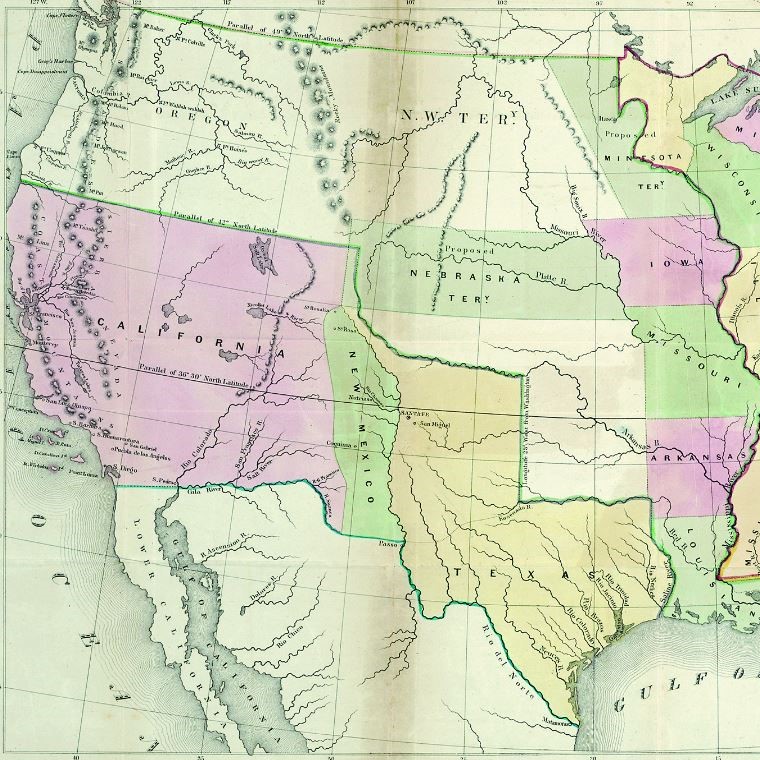
California was once part of Mexico. But after the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), and California was ceded to the United States. Very soon after, in 1948, the California Gold Rush began.
The California Gold Rush shaped California’s development and the American West.
But what if Mexico had retained control over California when gold was discovered? This hypothetical scenario raises intriguing questions about how different the Gold Rush and its consequences might have been under Mexican rule.
1. California Gold Rush: An Historical Background
The California Gold Rush of 1848 was a pivotal moment in American history, but its roots lie in the complex geopolitical landscape of the mid-19th century.
The event was preceded by the Mexican-American War (1846-1848). It was a conflict driven by territorial disputes and the United States’ expansionist ideology of Manifest Destiny.

Before the war, California was a sparsely populated Mexican territory.
Mexico had gained independence from Spain in 1821 and inherited a vast northern frontier, including California.
The Mexican government implemented policies aimed at settlement and resource management in these regions, but faced significant challenges in effectively controlling and developing such distant territories.
Meanwhile, the United States had been expanding westward throughout the early 19th century. This expansion was fueled by a belief in Manifest Destiny – the idea that American settlers were destined to expand across the North American continent.
As American settlers began moving into Mexican-controlled territories like Texas and California, tensions between the two nations escalated.
The annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845 further strained relations. Mexico still considered Texas part of its territory, and this action by the U.S. was seen as a direct challenge to Mexican sovereignty.
The dispute over the Texas-Mexico border ultimately served as the immediate trigger for the Mexican-American War.
The war began in 1846 and lasted until 1848.
Despite facing internal political instability and economic challenges, Mexico fought to maintain its northern territories. However, the United States, with its stronger military and economic position, gradually gained the upper hand.
The conflict culminated in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed on February 2, 1848.
This treaty ended the war and resulted in Mexico ceding nearly half of its territory to the United States, including California, Nevada, Utah, most of Arizona, and parts of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming. In exchange, the U.S. paid Mexico $15 million and assumed $3.25 million in Mexican debts to American citizens.
Ironically, just nine days before the treaty was signed, gold was discovered at Sutter’s Mill in Coloma, California.
This discovery would trigger the California Gold Rush, transforming the newly acquired territory and profoundly impacting the development of the American West.
The timing of this discovery adds a layer of historical intrigue, raising questions about how events might have unfolded had the gold been discovered while California was still under Mexican control.
2. The Discovery of Gold in California and Its Implications
While the California Gold Rush is often associated with the 1848 discovery at Sutter’s Mill. But it’s important to note that gold was first documented in California several years earlier.
In 1842, Francisco Lopez made the initial recorded discovery of gold at Rancho San Francisco, north of Los Angeles. This early find, however, did not immediately trigger the massive influx of prospectors that would later characterize the Gold Rush.
The more famous and impactful discovery occurred on January 24, 1848, when James W. Marshall found gold flakes in the American River at Sutter’s Mill in Coloma, California.

This event ignited a rush that would transform the region and have far-reaching consequences for the newly acquired U.S. territory.
Had California remained under Mexican control during these discoveries, the implications would have been profound.
The Mexican government, already grappling with political and economic instability, would have faced both a significant opportunity and a major challenge.
The gold discoveries would have presented a chance to boost the national economy and strengthen Mexico’s position on the world stage. However, managing the sudden influx of wealth and people would have posed considerable difficulties.
In response to the gold discoveries, the Mexican government might have attempted to establish stricter governance and increase military presence in California.
These measures would aim to control the influx of prospectors and protect the region’s valuable resources. The government might also have implemented policies to ensure that the wealth generated from gold mining benefited the Mexican state and its citizens.
The lure of gold would likely have attracted settlers from other parts of Mexico, potentially altering internal migration patterns and demographic distribution within the country.
News of the gold discoveries would have also spread internationally, potentially drawing prospectors from Europe, South America, and Asia, much like the actual Gold Rush did under U.S. control.
This international influx would have presented both opportunities and challenges for Mexico. On one hand, it could have led to rapid development and economic growth in California.
On the other, it might have strained Mexico’s ability to maintain control over the region and its resources, potentially leading to conflicts with foreign powers interested in accessing the gold.
The gold discoveries, if managed effectively, could have significantly altered Mexico’s economic trajectory and its standing in the global community.
However, the challenges of managing such a sudden and valuable resource discovery would have tested the Mexican government’s administrative capabilities and potentially exacerbated existing internal political tensions.
3. Potential Consequences and Challenges in California
A gold rush in Mexican-controlled California would have had significant implications across various aspects of Mexican society, politics, and international relations.
Let’s explore these potential consequences and challenges in detail:
Territorial Disputes and Conflicts
The presence of valuable gold resources in California would likely have exacerbated existing tensions between Mexico and the United States, potentially leading to:
- Further conflicts or negotiations over the territory
- Increased U.S. interest in acquiring California, possibly through military action or diplomatic pressure
- Interest from other nations in California’s gold, complicating Mexico’s control
- Potential for international alliances or rivalries centered around access to California’s resources
Mexico might have sought to strengthen its military presence in California to deter foreign intervention, but this could have strained its resources and potentially led to skirmishes or larger conflicts.
Internal Political and Social Tensions
Managing a gold rush would have placed significant strain on Mexico’s political system, potentially leading to:
- Conflicts over resource allocation and governance
- Debates over centralized versus local control of gold mining operations
- Political pressure to use gold revenues to address longstanding economic issues in other parts of Mexico
- Potential for corruption and power struggles among Mexican elites vying for control of gold resources
The sudden influx of wealth and population into California might have altered the balance of power within Mexico, potentially leading to calls for greater autonomy or even independence for the region.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities
While the gold rush could have provided a significant boost to Mexico’s economy, it would also have posed numerous challenges:
- Need for rapid infrastructure development in California to support mining operations
- Difficulties in regulating gold extraction and trade to ensure benefits for the Mexican state
- Potential for economic destabilization due to rapid influx of wealth
- Challenges in managing currency and preventing inflation
- Opportunities for economic diversification and industrial development
Proper management of these economic factors could have led to significant benefits for Mexico, potentially transforming it into a wealthier and more industrialized nation. However, mismanagement might have exacerbated existing economic woes and led to a “resource curse” scenario.
Interactions with Native American Communities
Like in the current time, the influx of prospectors would likely have led to conflicts with Native American communities in California:
- Displacement of indigenous populations from traditional lands
- Cultural clashes between Native Americans and incoming miners
- Potential for violence and forced relocation of indigenous groups
- Challenges for the Mexican government in mediating conflicts and protecting indigenous rights
Mexico’s ability to effectively manage these challenges would have depended on its political stability, administrative capacity, and willingness to invest in California’s development. The outcomes could have ranged from a strengthened, more prosperous Mexico to a scenario of increased internal strife and external pressure.
4. Alternate Historical Scenarios for Mexico
If Mexico had retained control over California during the Gold Rush, the course of North American history could have been dramatically altered. Let’s explore some of these potential scenarios:
Revised Mexican-American Relations
The retention of California by Mexico would likely have reshaped the outcome of the Mexican-American War:
- The war might have ended in a stalemate or with less territorial loss for Mexico
- The United States might have focused its expansionist efforts elsewhere, possibly towards the Caribbean or South America
- Ongoing tensions between Mexico and the U.S. could have led to further conflicts or a series of negotiations over access to California’s resources
California’s Development Under Mexican Rule
California’s growth under continued Mexican governance would likely have differed significantly from its historical trajectory:
- A stronger Mexican cultural influence would have persisted, potentially resulting in a more bilingual, bicultural society
- Economic development might have been slower initially, but could have accelerated as Mexico invested gold revenues into infrastructure and industry
- The influx of international migrants would have still occurred, but might have been more tightly controlled by the Mexican government
- Urban development patterns could have differed, with greater emphasis on existing Mexican settlements rather than new American-style cities
Shift in North American Power Dynamics
A gold-rich Mexico would have altered the balance of power in North America:
- Mexico could have emerged as a major economic power, rivaling the United States in influence
- European powers might have sought closer alliances with Mexico, potentially leading to a multipolar power structure in North America
- The United States’ “Manifest Destiny” ideology might have been challenged, altering the course of American expansionism
- Canada’s development and relations with its southern neighbors could have been affected, potentially leading to closer ties with Mexico as a counterbalance to U.S. influence
Impact on American Westward Expansion
The retention of California by Mexico would have significantly impacted American westward expansion:
- The timeline of settling the American West would likely have been delayed
- American settlers might have focused more on the Oregon Territory or pushed for expansion into other areas
- The concept of the American frontier and its role in shaping American identity might have evolved differently
Economic and Technological Developments
California’s integration into the Mexican economy could have led to different patterns of economic and technological growth:
- Mexico might have invested heavily in modernizing California’s infrastructure, potentially becoming a leader in areas like rail transportation
- California would have been more integrated into Mexico through infrastructure such as road and rail
- The gold revenues could have funded industrial development throughout Mexico, potentially accelerating its transition to an industrial economy
- Different patterns of trade might have emerged, with Mexico potentially developing stronger economic ties with Asia and South America
Global Implications
The ripple effects of a Mexican California could have extended globally:
- The global perception of Mexico as a nation would have been enhanced, potentially leading to greater Mexican influence in international affairs
- The gold rush might have attracted a different mix of international migrants, altering global migration patterns
- The economic center of gravity in North America might have shifted southward, potentially changing global trade routes and economic relationships
These alternate scenarios highlight the pivotal role that the California Gold Rush played in shaping not just regional, but global history. While speculative, they offer valuable insights into the complex interplay of factors that influence historical outcomes and the potential for seemingly localized events to have far-reaching consequences.
5. Final Thoughts on the ‘What If’ California Gold Rush scenarios
Exploring the hypothetical scenario of Mexico retaining control over California during the Gold Rush offers valuable insights into the complexities of historical events and their far-reaching consequences. This counterfactual analysis highlights how different governance, economic policies, and international relations might have shaped the development of California and the American West.
Understanding these alternative scenarios helps us appreciate the multifaceted nature of historical developments and the importance of considering various perspectives. The actual California Gold Rush was a transformative event that significantly impacted the region’s history, but imagining different outcomes underscores the contingent nature of history and the myriad factors that influence the course of events.
By reflecting on these hypothetical situations, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical forces at play and the potential paths not taken, enriching our appreciation of the past and its significance.
Further Reading
I hope you have found this blog post about What Was the California Gold Rush of 1849? interesting. To find out more about the California Gold Rush and other expansions of the United States, read here:
- What Was the California Gold Rush of 1849?
- What Ended the Gold Rush in California?
- Did the Spanish Find Gold in California?
- How Many People Died in the California Gold Rush?
- Who benefited the most from the California Gold Rush?
- Why Didn’t the United States Take All of Mexico?
- What US States Used to be Mexico?
- Why did Britain want Texas Independent?
You may also enjoy these articles exploring ‘What If’ scenarios: